iSMART: Implementation Strategies for Monitoring Adherence in Real Time for Oral Anticancer Therapies
- Augmented & Artificial Intelligence,
- Behavior Change,
- Clinical Transformation
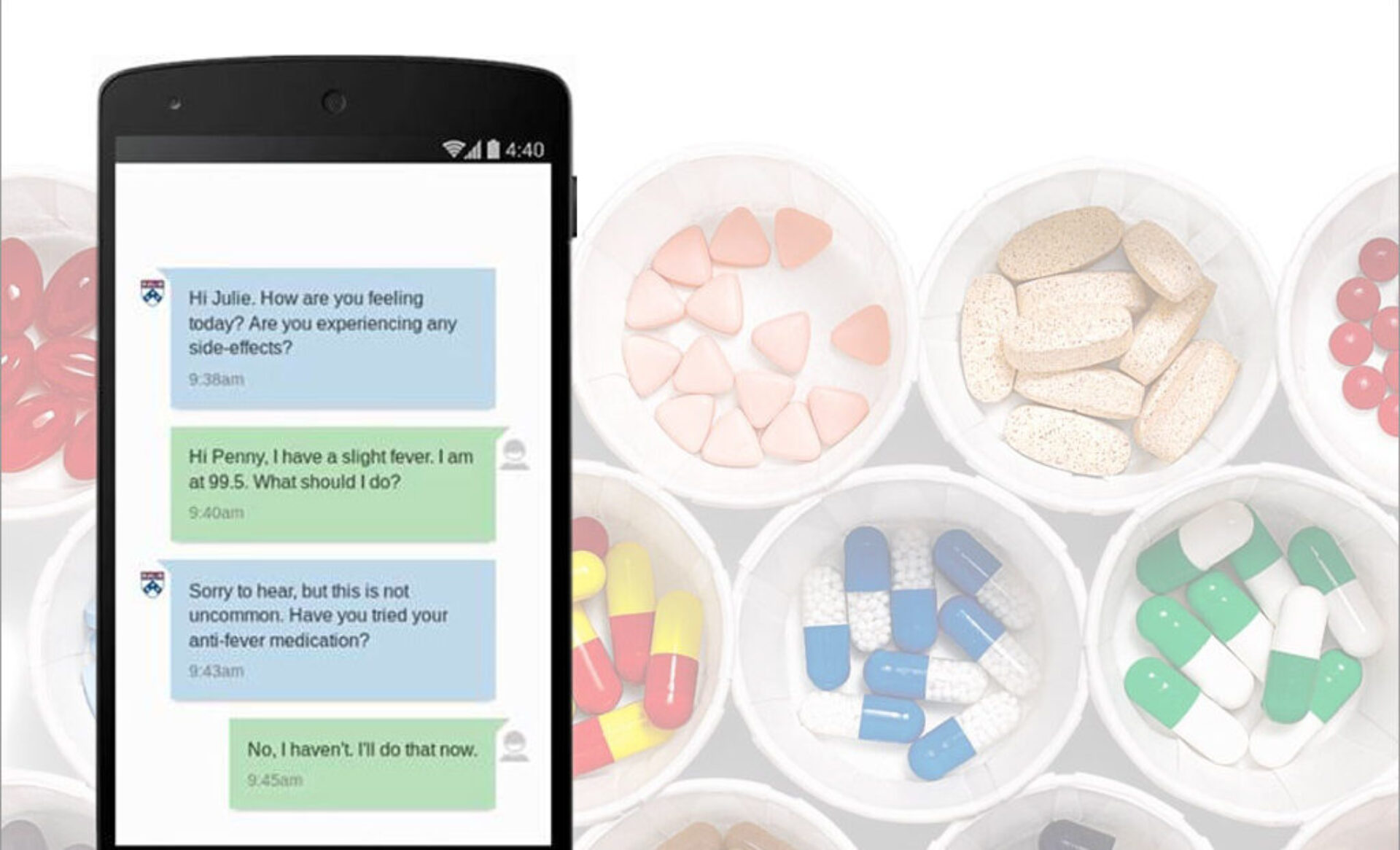
iSMART tested the effects of implementing a conversational chatbot to improve oral lung cancer treatment adherence & side-effect symptom management. Preliminary findings showed that patients with cancer who used the chatbot that patients had lower symptom burden and an increase of health-related quality of life.
Oral therapies in the treatment of lung cancer have unique side effect profiles that can lead to suboptimal adherence if not adequately managed, contributing ultimately to decreased effectiveness, increased toxicity, and higher costs.
The objective of the iSMART project is to identify effective strategies to help patients with lung cancer manage side effects and achieve optimal adherence to oral targeted therapies. To achieve this objective, a PC3I-led team of researchers evaluated the effects of a bidirectional, conversational agent on adherence using a two-arm randomized controlled trial, and explored factors shaping the acceptability and effectiveness of this strategy by collecting qualitative and quantitative data from patients and clinicians.
By combining innovations from behavioral economics and machine learning with highly accessible text-messaging platforms, this project’s potential lay not only in identifying scalable, patient-targeted strategies for improving adherence to oral therapies, but also in transforming the way cancer care is delivered and implemented.
Over the course of 18 months, 75 patients across 4 sites were enrolled, with 38 patients assigned to the intervention engaging with the chatbot. Preliminary findings presented at the 2023 ASCO Annual Meeting showed no significant differences in medication adherence; however, patients in the intervention arm saw a significantly greater decrease in symptom burden and increase in health-related quality of life when compared to patients receiving usual care. These results demonstrate the potential benefit of chatbots in symptom management and make a compelling case for further study.
Lung Cancer Research Foundation-Pfizer Competitive Research Grant Program
Abramson Cancer Center Cancer Control Program and the Departments of Medicine, Division of Hematology Oncology, Radiation Oncology, Family Medicine and Community Health, and Biostatistics, Epidemiology, and Informatics.
Project Leads
-

-

Samuel Takvorian
MD, MSHP
Deputy Director, PC3I & Director, PC3I's Program in Patient-Generated Health Data
Project Team
-
Charu Aggarwal
-
Justin Bekelman
-
Sarah Beucker
-
Abigail Blauch
-
Christine Cambareri
-
James A. Colbert
-
Linda Jacobs
-
Caleb Johnston
-
Stephen E. Kimmel
-
Corey Langer
-
Abigail Mandel
-
Bethany Mooney
-
Donna Pucci
-
Larry Shulman
-
Jocelyn Wainwright
-
E. Paul Wileyto
-
Deirdre Yarosh
